Paper Link: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation by Backpropagation (mlr.press)
Overall Structure
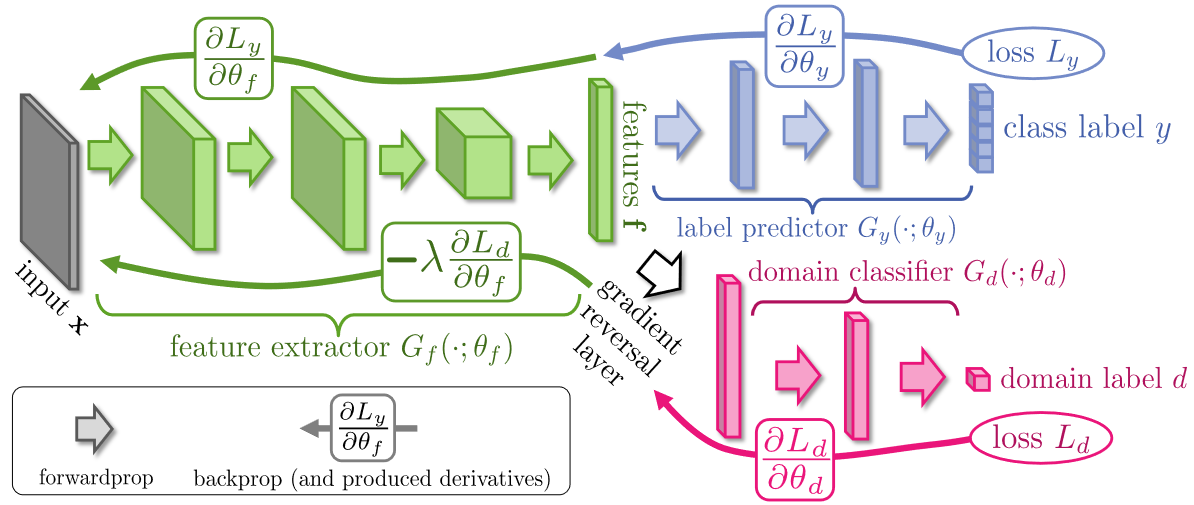
- Feature Extractor: Maps the source or target images to a feature vector
- Minimizes the source classification error
- Maximizes the loss of the domain discriminator (by making the two feature distributions as similar as possible so that the domain discriminator cannot tell whether the input is a source feature vector or a target feature vector)
- Label Predictor: Maps the source feature vector to a vector of class probabilities
- Minimizes the source classification error
- Domain Discriminator: Classifies whether the input feature vector is... read more

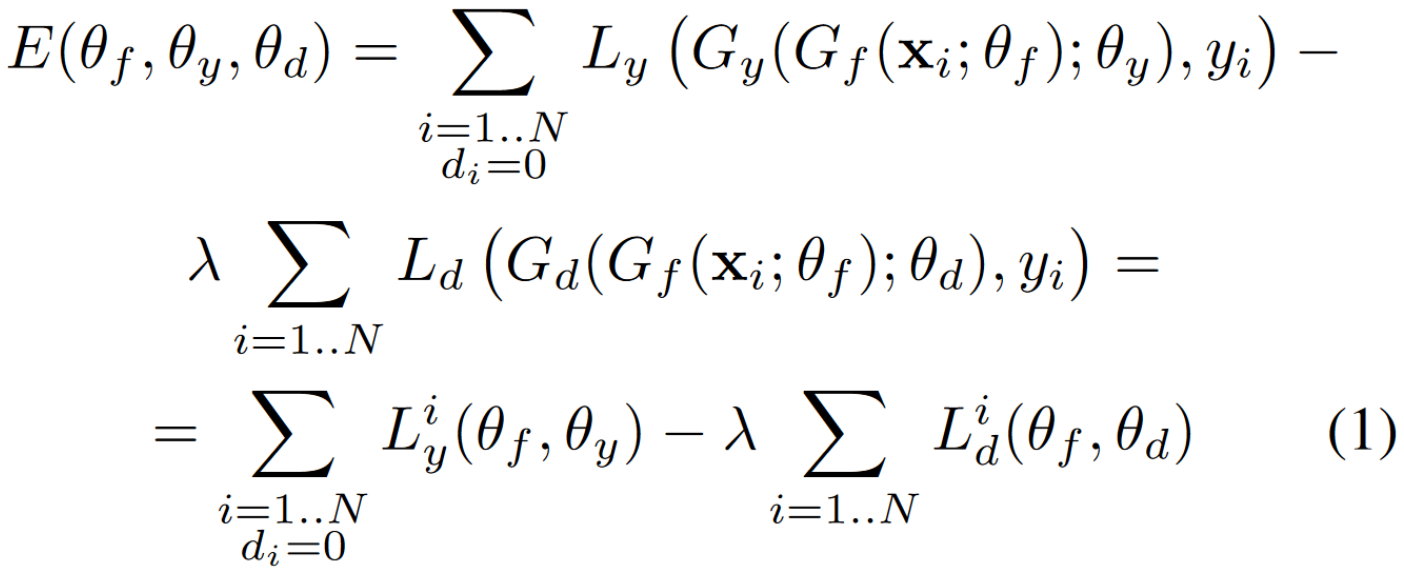
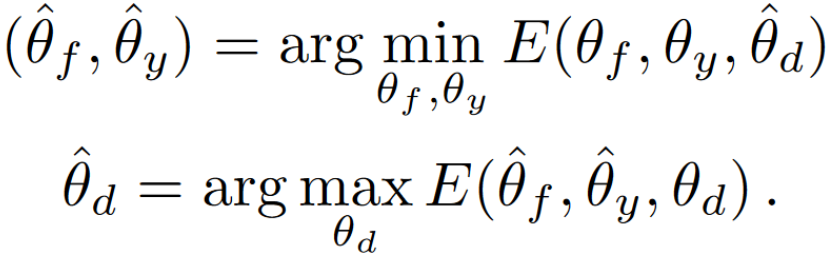
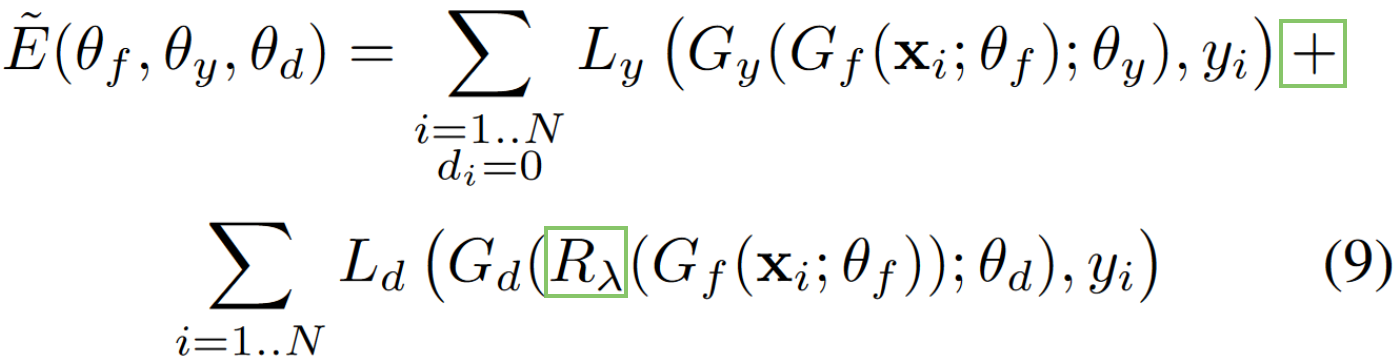

Comments